What Is An
Adverb?
An adverb
is a word that can modify a verb, an adjective, an adverb, or even a sentence. Adverbs
describe how, where, when, in what manner and to what extent something is done.
Adverbs are often formed by adding “-ly” to adjectives.
For example
Lora drives
carefully. She will arrive soon.
The words "carefully" and "soon" are adverbs.
Kinds of adverbs
There exist
eight kinds of adverbs:
- Adverbs of certainty
- Adverbs of degree
- Adverbs of frequency
- Adverbs of manner
- Adverbs of place
- Adverbs of time
- Interrogative adverbs
- Relative adverbs
Adverbs of certainty
Adverbs of
certainty indicate how certain we feel about an action. Adverbs of certainty can
go:
- Before main
verbs
- After verb
“to be”
- At the
beginning/ at the end of a sentence or clause.
Common adverbs of certainty:
Certainly,
surely, evidently, definitely, obviously, undoubtedly, apparently, clearly.
Examples
They have
certainly arrived.
He surely
won't forget them.
They are
certainly wonderful people.
Probably, I will meet them again.
Adverbs of degree
Adverbs of degree modify adjectives, adverbs and verbs. Adverbs of degree show us to what extent something is done. They are placed before the adjective, adverb or verb which they modify. The words "too", "so", and "extremely" are examples of adverbs of degree.
Adverb of degree modifying an adjective
For example
The task looks
too difficult.
Adverb of degree modifying an adverb
For example
They work extremely
motivationally !
Adverb of degree modifying a verb
For example
They nearly follow all his instructions!
Adverbs of frequency
Adverbs of frequency are used to describe how
frequent we do something. Adverbs of frequency are placed before the simple
tenses of verbs except for verb to be.
For example
She always
watches TV.
She is
always optimistic.
Examples of
adverbs of frequency.
Always, frequently,
occasionally, often, once, periodically, usually, never, regularly, seldom,
sometimes, etc.
Common adverbs of frequency
|
Frequency
percentage |
Adverb of
Frequency |
|
100% |
Always |
|
90% |
Usually |
|
80% |
Generally/normally |
|
70% |
Frequently/often |
|
50% |
Sometimes |
|
30% |
Occasionally |
|
10% |
Seldom |
|
5% |
Rarely/ hardly ever |
|
0% |
Never |
Common adverbs of frequency | Infographic
John always
goes to school.
He usually arrives
on time.
He seldom misses
a class.
John has
never failed a test.
Adverbs of manner
Adverbs of
manner show how something happens. They are usually placed either after the
main verb or after the object. The words "happily”, “quickly”, “well” are
examples of adverbs of manner.
Examples
She speaks fluently.
I read quickly.
They behave gently.
She waited
him patiently.
Adverbs of place
Adverbs of place show us where something takes place. Adverbs
of place are usually placed after the main verb or after the clause which they
modify. The words “here”, “above”, “behind” are called adverbs of
place.
For example
She is in
Italy, now.
Common adverbs of place
|
Common adverbs of place |
|
|
Abroad Across Ahead Away Back Backwards Beyond Down Downwards Eastwards |
Everywhere Here In Indoors Inside nearby Outside Overseas There West |
She’s going
back home.
Her parents
live nearby.
You can
go there.
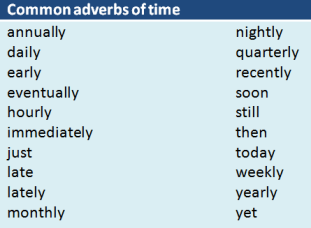
Adverbs of time
Adverbs
of time show us when an action occurred. The words “now”, “today”, “then” are
adverbs of time.
For example
She gets
paid hourly.
Common adverbs of time
|
Common adverbs of time |
|
|
annually daily early eventually hourly immediately just late lately monthly |
nightly quarterly recently soon still then today weekly yearly yet |
Interrogative adverbs
Interrogative adverbs are "why,"
"where," "when," and "how." The interrogative
adverbs are used to form questions.
Examples
Why are you
upset?
Where does
she work?
When did
you visit Madrid?
How did you
go there?
Relative adverbs
Relative
adverbs are “when”, “where” and “why”. Relative adverbs introduce relative
clauses.
- The relative adverb "when" is used to indicate time
For example
2002 is
the year when she visited us.
- The relative adverb "where" is used to indicate a place
For example
I know
the company where you work.
- The relative adverb "why" is used to indicate a reason
For example
- This is the reason why you should study English.
Forming adverbs
Regular adverbs
- Most adverbs are formed by adding “-ly” to the end of the adjective.
Examples
|
Adjective |
Adverb |
|
Smart Harsh Great |
smartly harshly greatly |
- Adjectives that end in “-y” change to “-I”
Examples
|
Adjective |
Adverb |
|
Greedy Heavy Happy |
greedily heavily happily
|
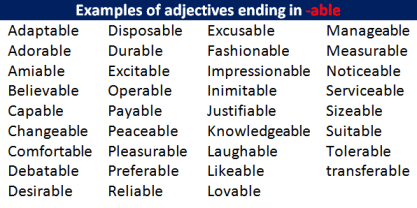
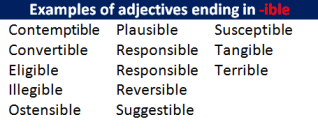
- Adjectives that end in -able/-ible drop the -e and add “-ly”.
Examples
Adjective | Adverb |
Readable Capable Flexible Incredible | readably capably flexibly incredibly |
Examples of adjectives ending in -able
|
Adaptable Adorable Amiable Believable Capable Changeable Comfortable Debatable Desirable |
Disposable Durable Excitable Operable Payable Peaceable Pleasurable Preferable Reliable
|
Excusable Fashionable Impressionable Inimitable Justifiable
Knowledgeable Laughable Likeable Lovable
|
Manageable Measurable Noticeable Serviceable Sizeable Suitable Tolerable transferable |
Examples of adjectives ending in -ible
|
Contemptible Convertible Eligible Eligible Illegible |
Ostensible Plausible Responsible Responsible Reversible |
Suggestible Susceptible
Tangible Terrible
|
Irregular Adverb
Irregular
adverbs are adverbs that do not follow the rules that control the regular
adverbs. Therefore, practice is key to use these irregular forms correctly.
Common irregular adverbs and their adjectival equivalents
|
Adjective |
Irregular Adverb |
|
Fast Hard Straight Lively Late Daily Early Friendly Timely good |
Fast Hard Straight Lively Late Daily Early ____ ____ well |
Examples of irregular adverbs
Tom acted very well today.
He reacted fast.
He always works hard
He usually wakes up early and goes to bed late.
His studio is open daily.
Comparison of adverbs
Levels of Comparison
Comparative and superlative.
Adverbs of one syllable:
Comparative: add –er to the adverb
For example
He is older
than her.
Superlative:
add –est to the adverb
For example
He is
the oldest student in the class.
Adverbs of two or more syllables:
Comparative: put more
before the adverb.
For example
He speaks more loudly than you.
Superlative: put most before the adverb.
For example
He speaks the most loudly in the office.
Irregular comparisons
Some adverbs form the comparative and the superlative forms irregularly.
|
Adverb |
Comparative |
Superlative |
|
Badly |
Worse |
Worst |
|
far |
Farther/further |
Farthest/furthest |
|
little |
Less |
Least |
|
Much |
More |
Most |
|
Well |
Better |
Best |
Examples
Mariahworks better than her friend Lucy.
She
studies in the farthest school in town.
Maria is
the best driver I have ever seen.



Comments
Post a Comment